What Is Asset Performance Management (APM)?
Asset performance management as the name suggests is the management of assets wherein the business goals are prioritized along with the existing assets and their availability of them. In simple terms, asset management brings together the insights from data capture, integration, visualization and analytics together for a common purpose – improving the reliability and availability of assets. APM is a major driver of digital transformation across industries. It aligns digital techniques in such a way that they transform reliability and business performance. This practice of managing asset performance helps organizations make sound decisions for the company.
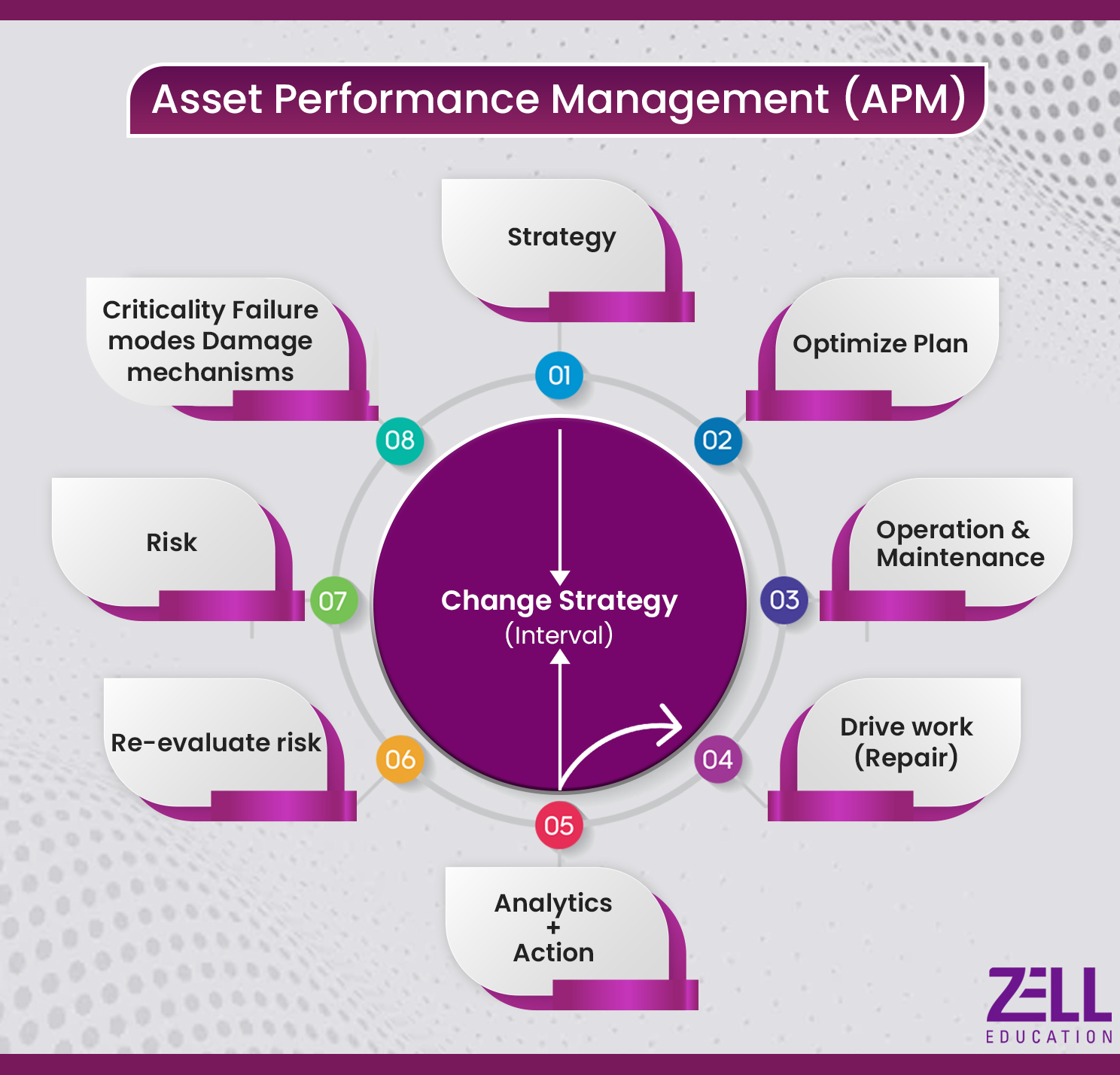
Key Components of Asset Performance Management
Asset Performance Management (APM) is a comprehensive approach to managing the lifecycle performance of physical assets to achieve business objectives effectively and efficiently. The key components of APM typically include:
Asset Strategy and Planning:
- Developing strategies and plans for managing assets throughout their lifecycle, including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal.
- Aligning asset management objectives with organizational goals and priorities.
Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance:
- Utilizing technologies such as sensors, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and data analytics to monitor asset health in real-time.
- Predicting potential failures or performance degradation to enable proactive maintenance actions, minimizing downtime and maximizing asset reliability.
Risk Management:
- Identifying and assessing risks associated with asset performance, including safety, environmental, operational, and financial risks.
- Implementing risk mitigation strategies to ensure asset reliability, compliance, and business continuity.
Reliability Engineering:
Applying engineering principles and methodologies to optimize asset performance and reliability.
Conducting reliability analysis, root cause analysis, failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) to improve asset reliability and availability.
Asset Health and Performance Analytics:
- Analyzing data collected from various sources to assess asset health, performance, and utilization.
- Using advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to derive insights, identify patterns, and optimize asset performance.
Lifecycle Asset Management:
- Managing assets throughout their entire lifecycle, from design and construction to operation, maintenance, and decommissioning.
- Considering factors such as total cost of ownership, asset value, regulatory compliance, and environmental sustainability.
Work Management and Optimization:
- Streamlining work processes and workflows related to asset maintenance, inspections, repairs, and replacements.
- Optimizing resource allocation, scheduling, and prioritization to maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
Performance KPIs and Reporting:
- Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure asset performance, reliability, availability, and utilization.
- Generating reports and dashboards to track performance trends, monitor compliance, and support decision-making.
What’s the Difference Between APM and CMMS?
Asset Performance Management:
As operations or management head, you’ll already have an insight into how and which of the organization’s assets would fail. With asset performance management, you can track the assets better and ensure minimal risk to critical operations. Tracked through advanced digital processes, the APM is enhanced with AI-powered insights, targeted automation and analytics. The AI offers several features like remote monitoring, computer vision, and perspective maintenance. Assets for a company could be anything, from systems of decisions to digital tools. Tracking their performance is essential to understand their return on investment and if maintenance is really worth it. It will also help understand when a particular asset is about to reach its last point and what can be reversed in terms of related risk involved.
CMMS on the other hand stands for Computerized Maintenance Management System. It’s a software solution used by organizations to manage and streamline maintenance operations for their assets and equipment. CMMS software typically offers a range of features designed to help organizations efficiently plan, schedule, track, and analyze maintenance activities.
Why is Asset Performance Management important?
Asset management is required for monitoring assets in a smarter and faster way. It also helps in predicting asset failure and planning the next steps. APM helps in ensuring that assets operate reliably and efficiently, minimizing downtime and production disruptions. By monitoring asset performance in real-time and predicting potential failures, maintenance activities can be optimized to prevent breakdowns and extend asset lifespan.
Optimizing Maintenance Strategies: APM enables organizations to move from reactive maintenance (fixing assets after they fail) to proactive and predictive maintenance strategies. This shift reduces maintenance costs, improves asset uptime, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Enhancing Safety and Compliance: By monitoring asset performance and identifying potential safety hazards or compliance issues, APM helps in mitigating risks and ensuring that assets meet regulatory standards. This promotes a safer work environment and reduces the likelihood of accidents or regulatory penalties.
Improving Decision-Making: APM provides actionable insights into asset health, performance trends, and maintenance needs. This data-driven approach empowers organizations to make informed decisions regarding asset investments, maintenance priorities, and resource allocation, leading to better overall business outcomes.
Increasing Asset Utilization: APM helps in optimizing asset utilization by identifying underutilized or idle assets and reallocating them effectively. By maximizing asset utilization, organizations can improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and enhance return on investment.
Supporting Business Continuity: By proactively managing asset performance and minimizing unplanned downtime, APM contributes to ensuring business continuity and resilience. This is particularly critical for industries where asset availability directly impacts production output, customer satisfaction, and revenue generation.
Facilitating Digital Transformation: APM leverages technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics to collect and analyze vast amounts of data from assets. This facilitates digital transformation initiatives by enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of asset operations in real-time.
How Should you Implement Asset Performance Management?
To implement asset management is where you’ll need a robust strategy that ensures seamless workflow of the company workings. Here are some of the top ways in which you can implement asset performance management.
- Firstly define the goals you have with asset performance management. Whether you’re looking to enhance product performance or reduce maintenance costs or even improve safety, you need to define what exactly it is that you’re looking for.
- Find out which assets directly impact the performance of the business and prioritize them accordingly.
- Collect real-time data through sensors and other modes to ensure smooth functioning of the assets. Also deploy training procedures for the management in charge of handling the assets.
Asset Performance Management Business Benefits
Here are some of the top benefits of including asset performance management into your business.
- Monitoring assets the smarter and faster way
- Predicting asset failure and planning the next steps
- Checking asset health and initiating maintenance activities
- Creating an asset strategy on the basis of accurate data
Performance Measurement and Control
1. Performance analysis in private sector organisations
- Describe, calculate and interpret financial performance indicators (FPIs) for profitability, liquidity and risk in both manufacturing and service businesses. Suggest methods to improve these measures.
- Describe, calculate and interpret non-financial performance indicators (NFPIs) and suggest methods to improve the performance indicated.
- Analyse past performance and suggest ways for improving financial and non-financial performance.
- Explain the causes and problems created by short-termism and financial manipulation of results and suggest methods to encourage a long-term view.
- Explain and interpret the Balanced Scorecard, and the Building Block model proposed by Fitzgerald and Moon.
- Discuss the difficulties of target setting in qualitative areas.
2. Divisional performance and transfer pricing
- Explain and illustrate the basis for setting a transfer price using variable cost, full cost and the principles behind allowing for intermediate markets.
- Explain how transfer prices can distort the performance assessment of divisions and decisions made.
- Explain the meaning of, and calculate, Return on Investment (ROI) and Residual Income (RI), and discuss their shortcomings.
- Compare divisional performance and recognise the problems of doing so.
3. Performance analysis in not-for-profit organisations and the public sector
- Comment on the problems of having non-quantifiable objectives in performance management.
- Comment on the problems of having multiple objectives in this sector.
- Explain how performance could be measured in this sector.
- Outline Value for Money (VFM) as a public sector objective.
- Describe, calculate and interpret non-financial performance indicators (NFPIs) and suggest methods to improve the performance.
- Discuss the difficulties of target setting in qualitative areas.
- Analyse past performance and suggest ways for improving financial and non-financial performance.
- Explain the causes and problems created by short-termism and financial manipulation of results and suggest methods to encourage a long-term view.
4. External considerations and behavioural aspects
- Explain the need to allow for external considerations in performance management, including stakeholders, market conditions and allowance for competitors.
Performance Management (PM)
- Suggest ways external considerations could be allowed in performance management.Interpret performance in the light of external considerations.
- Interpret performance in the light of external considerations.
Benefits of Asset Performance Management
- As operations or management head, you’ll already have an insight into how and which of the organisation’s assets would fail. With asset performance management, you can track the assets better and ensure minimal risk to critical operations. Tracked through advanced digital processes, the APM is enhanced with AI-powered insights, targeted automation and analytics. The AI offers several features like remote monitoring, computer vision, and perspective maintenance.
- Assets for a company could be anything, from systems of decisions to digital tools. Tracking their performance is essential to understand their return on investment and if maintenance is really worth it. It will also help understand when a particular asset is about to reach its last point and what can be reversed in terms of related risk involved.
Here are some of the top benefits of including asset performance management into your business.
- Monitoring assets the smarter and faster way
- Predicting asset failure and planning the next steps
- Checking asset health and initiating maintenance activities
- Creating an asset strategy on the basis of accurate data
Both ACCA and US CMA have Performance Management as a subject. Advanced Performance Management in ACCA includes calculation and interpretation of financial performance indicators (FPIs) for profitability, liquidity and risk in both manufacturing and service businesses. The Performance Management in US CMA includes variance analysis, labour, mix and yield variances, overhead and controllable variances, sales variances, variances for the service sector and market variances, etc.
Whether you choose a purely accounting course or a management course, performance tracking plays an important part. To know more about the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants or US Certified Management Accounting course you can click on the WhatsApp button at the side of this blog and get in touch with our experts directly.
FAQs
1. What does asset performance mean?
Asset performance management is a way of tracking operational assets while keeping their ROI in mind and planning maintenance activities accordingly. APM also helps in planning risk management activities in case of asset failure.
2. Why is asset performance management required?
Asset management is required for monitoring assets in a smarter and faster way. It also helps in predicting asset failure and planning the next steps.
3. What is the difference between EAM and APM?
Enterprise asset management includes the management of physical assets like raw materials, machinery, tools, etc. APM on the other hand is a process of tracking systems of decisions to digital tools.
4. What are the 3 pillars of asset management?
The pillars of asset management include people, processes and technology.
5. How do you measure asset performance?
Asset performance can be tracked using key performance indicators like effective equipment, asset utilization, mean-time between failures, mean-time to repair, downtime, maintenance cost, etc.
6. Is APM a good career?
Yes, asset performance management is a good career as brands look for ROI on each investment, especially assets. Tracking and managing is quite crucial for the business in every way.
7. Which APM tool is best?
IBM Maximo and GE Digital APM are some of the best asset performance management tools currently among the rest.
8. What is the salary of APM in India?
The starting salary of a fresher in APM starts from around 3LPA and for an experienced professional it goes up to 20 LPA.