Accounting is the most crucial element of a business. Financial accounting is the recording or procedure of creating documents containing all the essential details about the company’s operations and decisions. It gathers information and then distributes it to the stakeholders to ensure the company is managed with utmost transparency.
Let us dive deeper into the nitty-gritty of financial accounting.
What is Financial Accounting?
In simple terms, financial accounting is the process that accounts for every money that flows in and out of a company. The process involves recording, categorising and summarising every financial transaction.
There are various categories to define the different types of transactions:
- Revenue: It is usually derived from the selling of services or goods.
- Expenses: These are the business expenses, including office rent, salaries and other services.
- Assets: This is the worth of a business. Assets could be physical (tangible), such as property or equipment. Also, they can be intangible, like databases, software patents, clients, intellectual property, and so on.
- Liabilities: This is the amount a company has to pay. It’s not just about debt and outgoings but also projected expenses. Examples include payroll, mortgages and payments to suppliers.
- Equity: This is the amount left after subtracting assets from liabilities. It’s the money that the business’s owner and shareholders have.
Want to explore career options in accounting? Read our comprehensive guide on the Top 5 Accounting and Finance Careers After Graduation.
How Financial Accounting Works
Financial accounting works through a systematic process where every financial transaction is recorded, classified, and summarized to produce reports. These reports offer a snapshot of a company’s financial status, including the financial performance (profit or loss) and the financial position (assets, liabilities, and equity).
The steps involved in financial accounting are:
- Transaction Recording: Every financial transaction is documented, typically through invoices, receipts, or other relevant documents.
- Journal Entries: Transactions are recorded in journals, following the double-entry accounting system. Each transaction is entered as both a debit and a credit.
- Posting to Ledger: The journal entries are posted to a general ledger, which organizes the data by account type (revenue, expenses, assets, etc.).
- Trial Balance: The ledger balances are summarized in a trial balance to check for accuracy.
- Preparing Financial Statements: From the trial balance, businesses prepare financial statements like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Different Types of Financial Accounting
A business can track the transactions it makes in two different ways:
- Cash Accounting: This type of financial accounting is based on cash transactions. Therefore, every transaction is a credit and debit entry.
- Accrual Accounting: Most companies prefer this method of recording cash and other transactions. Accrual accounting focuses on recording transactions as and when they happen, regardless of the currency exchange.
Accrual Method vs. Cash Method
There are two primary methods of financial accounting for recording revenue and expenses: Accrual Accounting and Cash Accounting.
- Accrual Method: Revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not when money actually changes hands. This provides a more accurate financial picture and is required for most large businesses and publicly traded companies. For example, a company records a sale when a product is delivered, even if the customer has not paid yet.
- Cash Method: Transactions are only recorded when cash is exchanged. This method is simpler but doesn’t always provide an accurate representation of a company’s financial health. For instance, a company would record revenue only when the customer actually makes the payment, not when the product is delivered.
Read the complete list of Top 13 Accounting Courses In India – Get Online Certification.
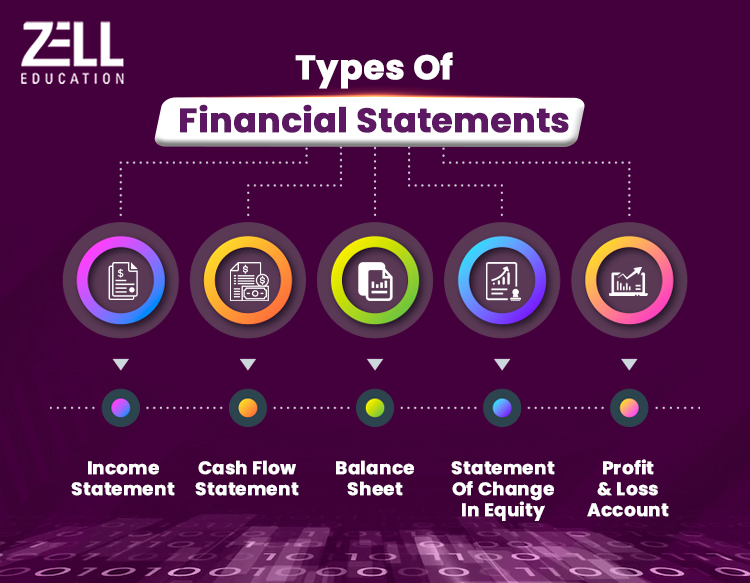
Different Types of Financial Accounting Statements
Financial statements organise information to provide a clear overview of the company’s financial situation. But no one statement can tell the entire story.
The following four kinds of statements create a complete picture of financial accounting:
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet can be described as a statement that outlines an organisation’s liabilities, assets and equity. Assets can include inventory, cash and equipment, investments, property, accounts receivable, and other accounts. The liabilities could consist of accounts payable, loans, tax due, paying mortgages, and non-earned income. Equity can include shareholder-owned stocks, retained earnings or total income.
Assets = Equity + Liabilities
Analysts, investors and shareholders use balance sheets to assess the financial condition of a business.
Income Statement
An income statement, or profit and loss report, accounts for an organisation’s net earnings over a time period. It is calculated by subtracting total costs from the total revenue. It will show profits, expenses and losses.
Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow statements are a thorough overview of the organisation’s revenue and liabilities. However, it is confined exclusively to cash transactions. Statements of cash flow are split into three parts which include investing activities and financing. When an income statement details the results, losses, gains as well as expenses, the statement does not address cash directly.
The cash flow is the amount of money an organisation can access at any time, indicating the sustainability of its operations and the profit it earns.
The report consists of three distinct types of cash flows:
- Operational activities- This is the case for selling items or services (money coming in) and salaries or supplier invoices (money being sent out).
- Investment activities- It tracks changes in a company’s assets, liabilities and cash equivalents. For example, the acquisition of new software could be reported within this area as cash-in since it’s an expense. Selling assets, such as equipment or property, is one example of cash-in.
- Financing activities- The cash flow statement details the money flowing in and out of bonds, loans, and investments.
Shareholders’ Equity Statement
A shareholder’s equity statement shows how equity fluctuates with time. It’s an addition to the balance sheet, which shows the equity at a particular time.
A statement of equity for shareholders includes additional information about the equity components:
- Share capital is the amount the company has raised through selling shares.
- Net profit is the company’s earnings after deductions and expenses.
- Dividends represent the proportion of profits that the company pays to shareholders.
- Retained earnings are the company’s earnings after it has paid dividends.
Learn about 5 Courses to Enhance your Accounting Career: Top Short-Term and Certification Courses.
Curious About The Types of Financial Accounting Statements?
Who Uses Financial Accounting?
There are multiple users who use financial accounting, as it helps them make informed decisions in their respective spheres. Here are some of the users who use financial accounting quite frequently.
- Customers
- Government agencies
- Creditors and lenders
- Employee and labour unions
- Top company management and internal stakeholders
Why Are Financial Statements Important?
Why are financial statements part of the financial accounting definition? They are a vital source of information for four key groups:
- Shareholders: Shareholders would like to know how their business is doing. If the financial results are poor, they could sell their shares in the company. In certain instances, particularly for smaller businesses, shareholders can request clarification or suggestions from management. Or, they could request a change in management.
- Potential investors: Investors looking for investment opportunities assess financial statements to determine which stocks to buy and at what price. They calculate metrics like the price-earning ratio (the stock price divided by profits per share). Since all publicly traded companies utilise GAAP accounting methods, shareholders can compare the ratios of different companies and decide on the most promising investment.
- Management Teams & Decision-Makers: Financial statements show the management teams how the business is doing and what’s working and what’s not. If the company has adjusted its operations or introduced innovative products or services, the financial reports can help determine the success of the efforts.
Principles of Financial Accounting
Financial accounting follows a set of universally accepted principles known as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). These principles ensure transparency, consistency, and comparability of financial statements. Key principles include:
- Accrual Principle: Revenue and expenses are recognized when they occur, not when cash is received or paid.
- Consistency Principle: Companies should apply the same accounting methods from one period to the next.
- Prudence Principle: Revenue and profits should only be recognized when they are earned, and not before.
- Going Concern Principle: Financial statements are prepared under the assumption that a business will continue to operate for the foreseeable future.
Who Uses Financial Accounting?
There are multiple users who use financial accounting, as it helps them make informed decisions in their respective spheres. Here are some of the users who use financial accounting quite frequently.
- Customers
- Government agencies
- Creditors and lenders
- Employee and labour unions
- Top company management and internal stakeholders
Who Uses Financial Accounting?
There are multiple users who use financial accounting, as it helps them make informed decisions in their respective spheres. Here are some of the users who use financial accounting quite frequently.
- Customers
- Government agencies
- Creditors and lenders
- Employee and labour unions
- Top company management and internal stakeholders
Why Are Financial Statements Important?
Why are financial statements part of the financial accounting definition? They are a vital source of information for four key groups:
- Shareholders: Shareholders would like to know how their business is doing. If the financial results are poor, they could sell their shares in the company. In certain instances, particularly for smaller businesses, shareholders can request clarification or suggestions from management. Or, they could request a change in management.
- Potential investors: Investors looking for investment opportunities assess financial statements to determine which stocks to buy and at what price. They calculate metrics like the price-earning ratio (the stock price divided by profits per share). Since all publicly traded companies utilise GAAP accounting methods, shareholders can compare the ratios of different companies and decide on the most promising investment.
- Management Teams & Decision-Makers: Financial statements show the management teams how the business is doing and what’s working and what’s not. If the company has adjusted its operations or introduced innovative products or services, the financial reports can help determine the success of the efforts.
Main Purpose of Financial Accounting
The main purpose of financial accounting is to provide financial information that is clear, accurate, and useful for decision-making. This includes enabling:
- Investors to assess a company’s profitability and potential for growth.
- Creditors to evaluate the company’s ability to repay debts.
- Management to make informed operational decisions.
- Regulatory Bodies to ensure compliance with financial reporting requirements.
Check out our blog on US CMA vs ACCA vs CIMA: Which Certification is Better? to plan your financial accounting career.
Financial Accounting vs. Managerial Accounting
While both financial accounting and managerial accounting deal with the financials of a company, they serve different purposes:
- Financial Accounting: Primarily focuses on producing financial statements for external users (investors, creditors, regulatory agencies). It is historical in nature, adhering to fixed standards like GAAP or IFRS.
- Managerial Accounting: This is more internally focused and helps management with decision-making. It includes budgeting, cost analysis, and financial forecasting, providing a more detailed look at the business’s operations and future prospects.
Professional Designations for Financial Accounting
For those pursuing a career in financial accounting, there are several certifications that can boost credibility and open doors to advanced career opportunities. Some key professional designations include:
- Chartered Accountant (CA): Recognized globally, CA is a prestigious qualification for accounting professionals in areas like auditing, taxation, and financial reporting.
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA): CPA certification A globally recognized qualification, particularly in the US, it focuses on areas like auditing, taxation, and accounting standards.
- Certified Management Accountant (CMA): CMA certification that blends financial accounting with management accounting, providing skills in both financial reporting and management decision-making.
Example of Financial Accounting
Let’s consider an example of how financial accounting works in a small business:
- Scenario: A company sells goods worth INR 1,00,000 on credit to a customer. The transaction is recorded in the company’s books under Accounts Receivable (asset) and Sales Revenue (revenue).
- Later, when the customer pays the invoice, the transaction is recorded as a cash inflow, and the Accounts Receivable is cleared. The business will reflect these transactions in the income statement and balance sheet to show the company’s performance and financial position.
Planning to Pursue Accounting and Finance Career?
To Book Your Free Counselling Session
Wrapping Up
Companies use financial accounting to keep track of their financial transactions. Businesses worldwide employ professionals trained and skilled in financial accounting principles and practices to achieve this. Globally-recognised CMA and ACCA certification can open the doors for a lucrative career as an accounting professional. Check out ACCA and CMA courses from Zell Education today and build a thriving career in accounting.
FAQs on Financial Accounting
What is financial accounting, and what is its example?
Financial accounting is the process of recording, summarising and reporting the revenue-expense generation and transactions of a company. The income statement of a company is an example of financial accounting.
What is the main purpose of financial accounting?
Financial accounting aims to record a company’s financial transactions over time. Different types of financial accounting statements help in the process and dues. Accounting professionals follow their own Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to create income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and shareholder’s equity reports.
What are the 4 types of financial accounting?
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement), Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position), Cash Flow Statement and Statement of Changes in Equity (Statement of Shareholders’ Equity).
What is the role of financial accounting?
Financial accounting involves systematically recording all financial transactions of a business, including sales, purchases, expenses, revenues, and investments. These transactions are recorded in accounting journals and ledgers using double-entry accounting principles to ensure accuracy and completeness of financial records.