The Differences Between IFRS and GAAP
In the field of accounting, there are two widely recognized sets of standards that are used globally to maintain uniformity and accuracy in financial reporting which are the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Both IFRS and GAAP have their own unique characteristics and rules that companies must adhere to when reporting their financial statements. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between IFRS and GAAP and the benefits of pursuing a diploma in IFRS.
IFRS Course Details
Before diving into the differences between IFRS and GAAP, let’s take a look at some IFRS course details. Pursuing a diploma in IFRS is a great way to enhance your accounting knowledge and skills, and make yourself more marketable to potential employers. An IFRS course typically covers a range of topics, including the structure and framework of IFRS, financial statement preparation, and the application of IFRS to specific industries. The duration of an IFRS course can vary depending on the institution, but it typically ranges from three to six months. The eligibility criteria for an IFRS course may also vary, but generally, applicants are required to have a basic understanding of accounting principles and concepts.
What is IFRS vs GAAP?
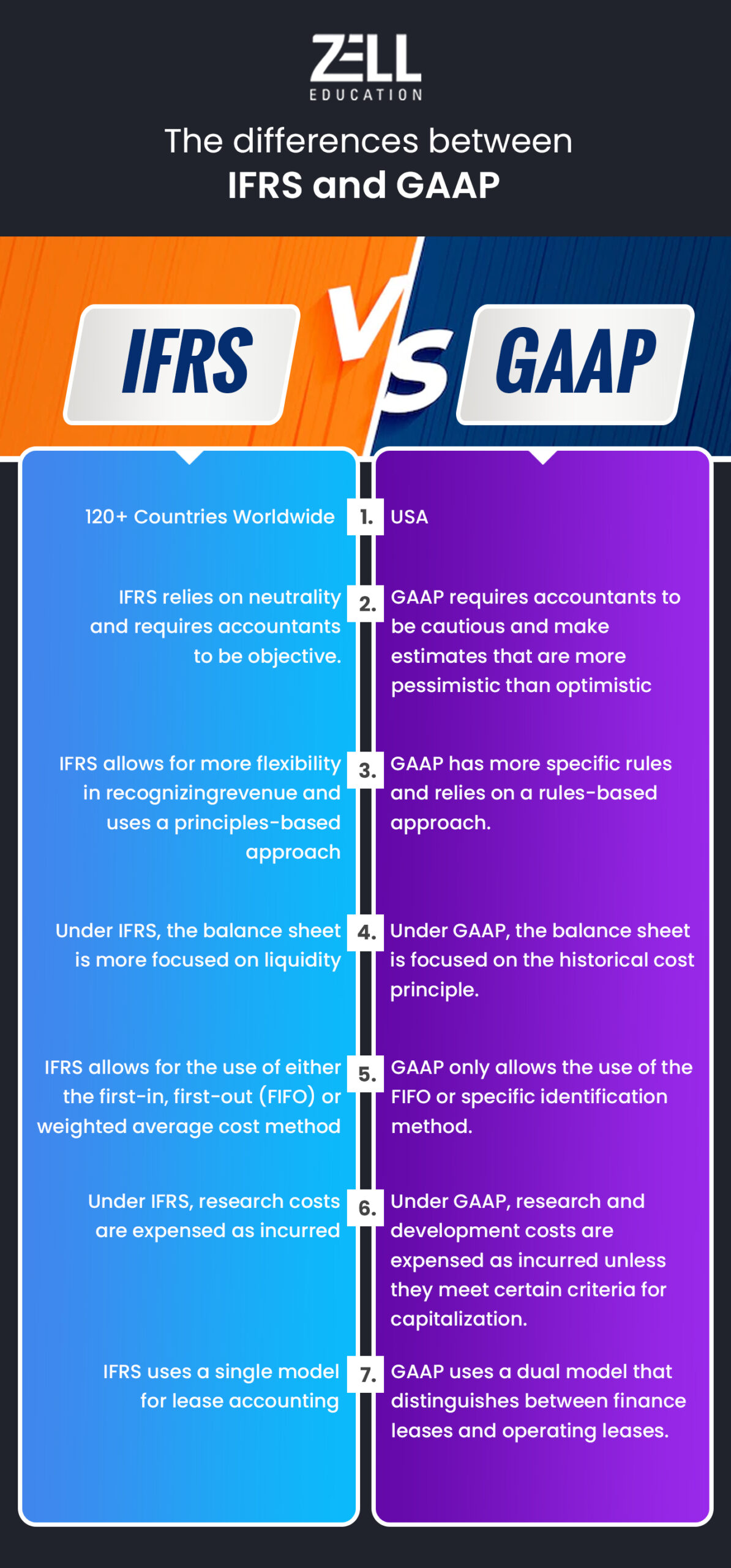
The accounting world has two standard sets for financial reporting: International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). GAAP maintains financial trust while IFRS helps in maintaining transparency in economy. Also, GAAP is mostly used in the USA while IFRS is used in as many as 132 jurisdictions globally..
Definition of Terms:
Before discussing the differences between IFRS and GAAP, let us understand both the terms individually.
IFRS
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a certification course offered by the ACCA body. The course aims at training candidates in accounting skills. The IFRS course covers several topics like the IFRS framework and structure, IFRS application, financial statement preparation, and similar. Candidates who have basic knowledge in accounting can attempt to pursue the IFRS course. The IFRS course duration is of 3 to 6 months.
GAAP
The Financial Accounting Standards Board issues and revises the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). The same body also offers certification after the course to the candidates. The certification course of 6 months focuses on recognition, presentation, measurement, and similar topics for different ASUs and ASCs. The GAAP course is perfect for professional accountants, finance managers, MBA professionals, and other accounting graduates,
Key Differences Between IFRS vs GAAP
Here is a differentiation between IFRS and GAAP based on some prominent factors.
Treatment of Inventory
The first difference is based on the inventory treatment. IFRS treats inventory at Net Realizable Value, but GAAP treats inventory at Net Asset Value.
Intangibles
The next factor that lays a ground for differentiation between IFRS and GAAP is the intangibles. IFRS recognises only those intangible assets that have economic value in the future. On the other hand, according to GAAP, companies must report the intangibles at a fair value.
Rules vs Principles
IFRS is based on principles, but GAAP is more based on a set of rules that may change occasionally. As IFRS is based on principles, it is flexible and allows companies to work freely in many situations. GAAP is not very flexible because it binds the operations through a set of rules. Also, the FAS Board may change the GAAP rules as and when required. So, the companies working on the GAAP fundamentals should remain updated with the latest set of GAAP rules.
Recognition of Revenue
According to IFRS, recognition of revenue only happens on delivery of value. GAAP has different rules of revenue recognition for different industries. Of course, the revenue recognition depends upon delivering a good or service.
Classification of Liabilities
IFRS and GAAP are different in terms of liabilities, too. For example, GAAP may hold those instruments as equity that are considered a financial liability by IFRS. Similarly, some instruments considered equity by IFRS may not be equity according to GAAP.
Both IFRS and GAAP have their fundamentals, principles, and standards. Both of them are short-term courses that enable the candidates to master in different areas of accounting.
Candidates can earn an average salary of Rs. 23.5 lacs per annum after completing GAAP course. On the other hand, candidates with IFRS certification earn Rs. 24 lacs per annum according to 6figr.com. Zell Education will help you understand the courses better and choose the correct one according to your future aspects.
Career Growth
Understanding the differences between IFRS and GAAP is essential for accounting professionals who want to expand their career opportunities. Companies that operate globally often prefer employees who are knowledgeable about both sets of standards, as it makes it easier to reconcile financial statements and comply with different regulatory requirements. Pursuing a diploma in IFRS can be an excellent way to demonstrate your knowledge and skills to potential employers and position yourself for career growth.
Read this blog to know more about IFRS Career Scope
Conclusion
In summary, IFRS and GAAP are two sets of accounting standards that are used globally to maintain consistency in financial reporting. While there are several differences between IFRS and GAAP, understanding these differences is crucial for accounting professionals who want to excel in their careers. Pursuing a diploma in IFRS can be an excellent way to enhance your knowledge and skills, and make yourself more marketable to potential employers. So, if you are interested in advancing your accounting career, consider enrolling in an IFRS course today! Reach out to us at Zell Education, and we’d be happy to counsel you.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between IFRS and GAAP?
The main difference between IFRS and GAAP is their mode of working. IFRS is principle- based, while GAAP is rule-based. Also, there are many other differences, like IFRS is flexible but GAAP is prescriptive. Apart from this, IFRS offers flexibility in asset valuation, while GAAP focuses on the asset’s historical cost.
2. What are the 4 standards of IFRS?
The 4 standards of IFRS are first-time adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards, Share-based payment, Business Combinations, and Insurance Contracts.
3. What are the principal differences between IFRS and Indian GAAP?
The principal difference between IFRS and Indian GAAP is that IFRS is based on international accounting standards. It guides companies in reporting different transactions in their financial statements according to the country where the company is based. Indian GAAP guides companies to follow rules developed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in India for business houses and organizations.